When central bankers are labeled as “hawkish” or “dovish,” it gives us a glimpse into their potential impact on the economy. These terms indicate whether they are more focused on combating inflation or stimulating economic growth. Their decisions can influence everything from your personal finances to job opportunities. So, what distinguishes these approaches, and why do investors pay such close attention when there’s a shift in sentiment? Understanding these dynamics is essential. In this article, we will discuss about Hawkish vs Dovish in trading.
Defining Hawkish and Dovish Monetary Policies

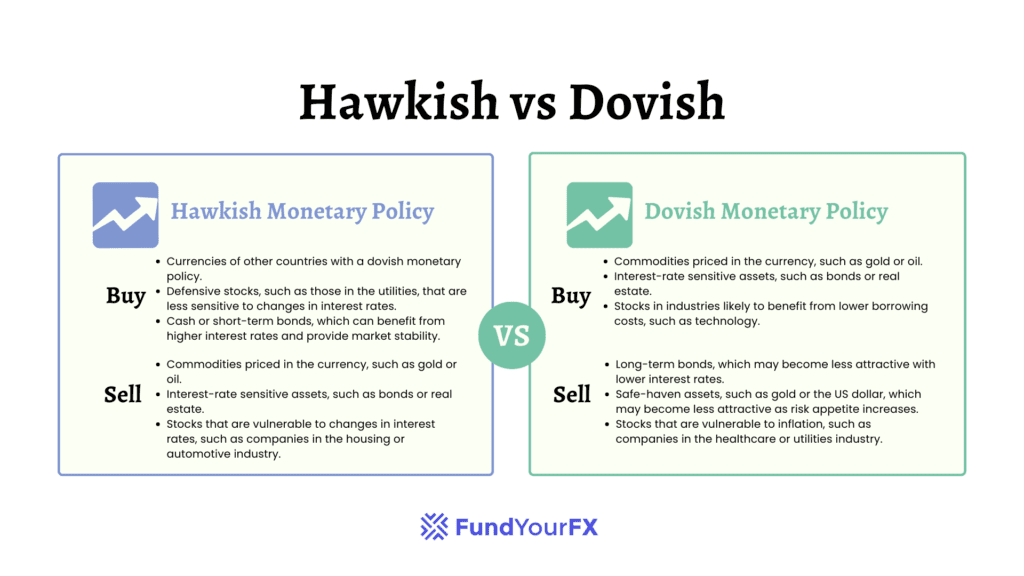
Central banks utilize hawkish and dovish monetary policies to influence the economy. A hawkish stance indicates that the central bank prioritizes controlling inflation. In this case, they tend to raise interest rates and tighten the money supply, which makes loans more expensive and can slow consumer spending. This approach helps maintain price stability but may also hinder economic growth. Traders closely monitor central bank policies to anticipate currency movements and market reactions. Effective risk management, such as setting stop-loss orders, becomes especially important for traders when markets react sharply to hawkish policy shifts.
Conversely, a dovish policy suggests that the central bank aims to stimulate economic activity and reduce unemployment. In this scenario, they lower interest rates and increase the money supply, encouraging borrowing and spending. While this can drive growth, there’s a risk of inflation rising if demand becomes excessive.
Central banks adjust these strategies in response to changing economic conditions, balancing the need for growth with the necessity of controlling inflation.
What is the Difference Between Hawkish and Dovish?
When examining hawkish and dovish strategies, the key difference is in their approach to inflation and economic growth. What is Hawkish vs Dovish meaning? A hawkish stance prioritizes controlling inflation, often leading to increased interest rates and a slowdown in economic activity. Hawks are firm believers in maintaining price stability, which means they’re prepared to accept slower growth to keep inflation under control. This can be seen when central banks, such as the European Central Bank, repeatedly raise rates to address persistent inflation. Market conditions, measured by economic indicators, often influence whether a hawkish approach is deemed necessary to address inflation risks.
In contrast, a dovish approach emphasizes economic growth and job creation. Doves advocate for lowering interest rates and expanding the money supply, even if it means allowing for higher inflation. Their focus is on stimulating spending and reducing unemployment, suggesting that a thriving economy can sometimes take precedence over strict inflation controls.
Ultimately, hawks tighten monetary policy to help cool down an overheating economy, while doves prefer to loosen it to encourage greater economic activity.
This balance is crucial, as it reflects the ongoing needs of the economy and the priorities of policymakers. Central banks often consider market volatility when deciding whether to adopt a hawkish or dovish stance in response to changing economic conditions.
Why Is It Called “Hawkish”?
When people talk about “hawks” in the context of government or finance, they’re referring to individuals or policies that take a tough, aggressive approach. For example, in monetary policy, a hawkish stance means being strict about inflation, often favoring higher interest rates to keep prices in check. In military or political situations, hawkish policies are more confrontational and ready to use force if necessary, much like the sharp and assertive nature of hawks—the birds of prey these terms are named after.
On the other hand, “doves” represent the opposite attitude. Dovish policies are cautious, gentle, and aim for peace or compromise. In economics, a dovish approach means prioritizing growth and employment, sometimes accepting higher inflation to avoid raising interest rates too quickly. In international relations, doves prefer diplomatic solutions over military action, reflecting the peaceful symbolism of doves.
Can Hawks Become Doves and Vice Versa?
Over the years, the leaders of the U.S. Federal Reserve have shown that their approach to monetary policy can shift. For example, Alan Greenspan started out with a reputation for being strict on inflation when he took over in 1987, but his stance became more flexible as time went on. Ben Bernanke, who led the Fed from 2006 to 2014, also moved between being more cautious and more accommodating depending on the economic situation.
Janet Yellen, who was in charge from 2014 to 2018, favored keeping interest rates low to support growth, earning her a reputation as someone who preferred looser monetary policy. The current chair, Jerome Powell, who took the position in 2018, is generally seen as balanced, neither particularly strict nor overly lenient.
This history shows that Fed leaders can adapt their approach, responding to changing economic conditions rather than sticking to a single philosophy.
Is Hawkish Good or Bad?
Whether being “hawkish” is good or bad really depends on the situation. In economics, a hawkish approach—like raising interest rates—is helpful when inflation is high, as it helps keep prices stable, but it can hurt the economy if growth is already weak. In politics or foreign affairs, a hawkish stance can protect security in the face of real threats but may also lead to unnecessary conflict if used too aggressively. So, being hawkish isn’t inherently good or bad; it can be the right or wrong approach depending on the problem at hand and the broader context.
Does hawkish mean up or down?
In finance, the term “hawkish” doesn’t directly mean “up” or “down,” but it signals a preference for raising interest rates to control inflation. When central banks or policymakers are described as hawkish, it usually means they are likely to increase interest rates (so, rates go up). This can make the country’s currency stronger (up), but it often leads to stock prices going down, since higher rates can hurt company profits and make stocks less attractive. So, “hawkish” mainly means interest rates are expected to go up, but it can mean prices of some assets, like stocks, might go down.
Economic Impacts on Consumers, Investors, and Businesses
When central banks implement a hawkish approach, it leads to higher interest rates. This means that mortgages and auto loans become more costly, prompting many to reduce their spending. Consequently, businesses might slow down their hiring and expansion plans due to the increased costs of borrowing. Understanding how leverage risk influences borrowing decisions can help both consumers and businesses better manage potential financial challenges during periods of higher rates.
For investors, a hawkish shift often results in a greater focus on bonds or other fixed-income investments, as rising rates can negatively affect stock market returns.
Conversely, a dovish stance results in lower interest rates, making borrowing more affordable. This encourages consumers to spend and invest more freely, while businesses benefit from easier access to credit, allowing them to expand and hire, which in turn stimulates economic activity.
A key element in monetary policy decisions is risk management in forex, as central banks assess potential risks to economic stability and adjust their strategies to protect overall growth.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hawkish Policies
While both hawkish and dovish monetary policies influence economic conditions, each comes with distinct trade-offs that can impact your financial choices.
If you prioritize stability and a strong currency, hawkish policies can help control inflation and maintain your purchasing power. However, these policies often lead to higher interest rates, which can slow economic growth, increase unemployment, and make borrowing more costly for individuals and businesses alike. Practicing risk management strategies is especially important in such environments to limit potential losses and protect your investments. When the market is volatile due to policy shifts, understanding concepts like support and resistance levels can also help you identify strategic entry and exit points.
Conversely, dovish policies tend to lower interest rates and expand the money supply, making it easier to borrow and invest. This approach can stimulate economic growth and create jobs, but if implemented for too long, it may result in higher inflation and lower returns on savings.
As you consider your investment strategies and financial planning, it’s essential to weigh these policy positions and their respective advantages and challenges. Adopting effective money management strategies is also crucial when navigating changing economic environments shaped by central bank decisions.
How to Trade Based on Hawkish vs Dovish
| Asset Class | Strategy | Example |
| Forex | Buy the central bank’s currency | Long USD/JPY, Short EUR/USD |
| Bonds | Short government bonds (expecting yields to rise) | Short U.S. Treasuries |
| Equities | Shift to value or defensive stocks; consider financials | Buy financials, avoid high-growth tech |
How to Trade Dovish Signals
| Asset Class | Strategy | Example |
| Forex | Sell the central bank’s currency | Long EUR/USD, Short EUR/JPY |
| Bonds | Buy government bonds (expecting yields to fall) | Buy U.S. Treasuries |
| Equities | Favor growth and risk-on assets (e.g., emerging markets, tech stocks) | Buy tech stocks, emerging market equities |
Market Reactions to Policy Shifts

Understanding the pros and cons of hawkish versus dovish monetary policies is vital to grasp how markets respond when central banks adjust their strategies. When a central bank adopts a hawkish stance, it usually signals potential interest rate hikes. This can lead to increased volatility in equity markets as investors brace for the impact on corporate profits and face higher borrowing costs. Additionally, traders who engage in CFD trading can quickly speculate on these price movements without owning the underlying assets, amplifying both opportunities and risks.
Consequently, many investors may pivot to safer assets like bonds, creating a “risk-off” environment that often results in falling stock prices.
Conversely, dovish signals from a central bank tend to invigorate the markets. Lower interest rates can stimulate spending and investment, making stocks more appealing. This typically sparks market rallies as investors become more optimistic about economic growth.
However, the intensity of these market reactions can vary significantly based on the broader economic context, such as prevailing inflation rates or unemployment levels, which influence how traders respond to policy changes. In 2024, rapid technological investments and market data advancements are also influencing how quickly and efficiently traders react to central bank policy shifts.
Conclusion
Understanding hawkish and dovish monetary policies is key to grasping central bank decisions and their impact on your finances. Each approach influences inflation, economic growth, and market dynamics differently. By recognizing these effects, you can better navigate fluctuations in interest rates and identify investment opportunities.
It’s vital to pay attention to policy signals, as changes between hawkish and dovish stances can influence various aspects of your financial life, from savings to employment prospects. Staying informed about these shifts provides a significant advantage in today’s rapidly changing economy.